trigonal pyramidal 3d drawing wedges
Molecular geometry in chemistry is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms that establish a molecule. It includes the full general shape of the molecule besides as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and whatsoever other geometrical parameters that decide the position of each atom.
Understanding the molecular structure of a compound can help make up one's mind the polarity, reactivity, phase of affair, color, magnetism besides as the biological activity. Molecular geometries have into account the number of atoms and the number of lone pair electrons. Common molecular geometries include:
- Linear
- Trigonal
- Tetrahedral
- Octahedral
Molecular geometries are adamant by the Valence-vanquish electron repulsion (VSEPR) theory. This is a theory that proposes the geometry of a molecule based on minimizing the repulsion between electron pairs. This model is useful for most compounds with a central atom. A table of geometries using the VSEPR theory can facilitate cartoon and agreement molecules.
Electrons, whether bonded or in solitary pairs will repel each other and they arrange around a cardinal atom in a way that minimizes this repulsion and maximizes the altitude betwixt them. Lone pairs of electrons volition repel stronger than bonded ones and this will change the bonded angles in the molecular geometry, making the angles slightly smaller.
Trigonal Planar
Trigonal planar is a molecular shape that results when at that place are three bonds and no alone pairs around the cardinal cantlet in the molecule. In an ideal Trigonal planar species, all iii ligands are identical and the pairs are bundled along the central atom's equator, with 120o bond angles between them. Molecules with a Trigonal planar electron pair geometries have sp2d hybridization at the central atom.
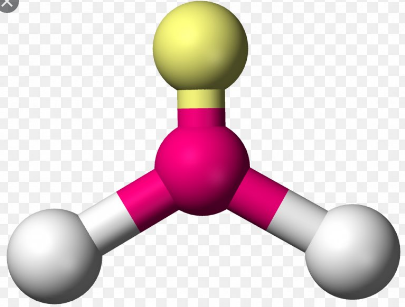
Examples of molecules with Trigonal planar geometry include:
- Boron trifluoride (BF3)
- Formaldehyde (H2CO)
- Phosgene (COCl2)
- Sulfur trioxide (SO3)
Ions with Trigonal planar geometry include:
- Nitrate (NOiii -)
- Carbonate (CO3 2- )
- Guanidinium (C(NHii )three + )
What You Need To Know About Trigonal Planar
- Trigonal planar geometry is shown past molecules with iv atoms. There is i central atom and the other three atoms (peripheral atoms) are connected to the central atom in a manner that they are in the corners of a triangle.
- In Trigonal planar, at that place is absenteeism of lone pair electrons in the central atom.
- Molecules with the Trigonal planar shape are triangular and in i plane or flat surface.
- A molecule with an ideal Trigonal planar geometry has an bending of 120o betwixt the peripheral atoms.
- Examples of atoms that bear witness Trigonal planar geometry include Boron trifluoride (BF), COCLtwo, carbonates, sulfates etc.
- In Trigonal planar, there is merely bond-bond repulsion.
Trigonal Pyramidal
Trigonal pyramidal is a molecular shape that results when there are three bonds and 1 lone pair on the central atom in the molecule. In organic chemistry, molecules which take a Trigonal pyramidal geometry are sometimes described as sp3. Ammonia (NHthree) is a Trigonal pyramidal molecule. It has three hydrogen atoms and the unshared pair of electrons attached to the nitrogen cantlet.
The three hydrogen atoms are repelled past the electron lone pair in a manner that the geometry is distorted to a Trigonal pyramid, thus, the 3 hydrogen atoms and the lone electron pair are as far autonomously as possible at nearly 109o bail angle.
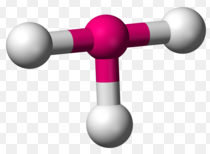
Examples of atoms that show Trigonal pyramidal geometry include:
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Chlorate ion (CIO3 – )
- Sulfite ion (And sothree two- )
- Pnictogen hydrides (XH3)
- Xenon trioxide (XeO3)
What You Need To Know Near Trigonal Pyramidal
- Trigonal pyramidal geometry is shown by molecules having four atoms or ligands. Fundamental atoms will be at the apex and three other atoms or ligands will be at 1 base, where they are in the three corners of a triangle.
- In Trigonal pyramidal, there is presence of i solitary pair electrons at the central atom.
- Atoms in Trigonal pyramidal are non in one plane.
- In Trigonal pyramidal, the bonded three atoms and the lone pair electron will exist as far apart as possible due to bond repulsion. The angle between the atoms volition be less than the angle of a tetrahedron (109o). Usually, the angle in a Trigonal pyramidal is around 107o.
- Examples of atoms that testify Trigonal pyramidal geometry include Ammonia, chlorate ion and sulfite ion.
- In Trigonal pyramidal, at that place is bail-bond, and bail-lone pair repulsion.
Also Read: Difference Betwixt SN1 And SN2 Reaction
Divergence Betwixt Trigonal Planar And Trigonal Pyramidal In Tabular Grade
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | TRIGONAL PLANAR | TRIGONAL PYRAMIDAL |
| Description | Trigonal planar geometry is shown by molecules with iv atoms. There is ane central atom and the other 3 atoms (peripheral atoms) are continued to the fundamental atom in a style that they are in the corners of a triangle. | Trigonal pyramidal geometry is shown past molecules having four atoms or ligands. Central atoms volition be at the apex and three other atoms or ligands will be at i base, where they are in the iii corners of a triangle. |
| Solitary Pair Electrons | In that location is absence of lone pair electrons in the central atom. | At that place is presence of one alone pair electrons at the central cantlet. |
| One Plane | Molecules with the Trigonal planar shape are triangular and in one plane or flat surface. | Atoms in Trigonal pyramidal are not in 1 airplane. |
| Bond Angle | A molecule with an ideal Trigonal planar geometry has an angle of 120o between the peripheral atoms. | The bond angle in a Trigonal pyramidal is effectually 107o. |
| Examples | Boron trifluoride (BF), COCLii, carbonates, sulfates etc. | Ammonia, chlorate ion and sulfite ion. |
| Bond Repulsion | There is only bond-bond repulsion. | There is bond-bond, and bond-alone pair repulsion. |
Source: https://vivadifferences.com/difference-between-trigonal-planar-and-trigonal-pyramidal-geometry/
0 Response to "trigonal pyramidal 3d drawing wedges"
Post a Comment